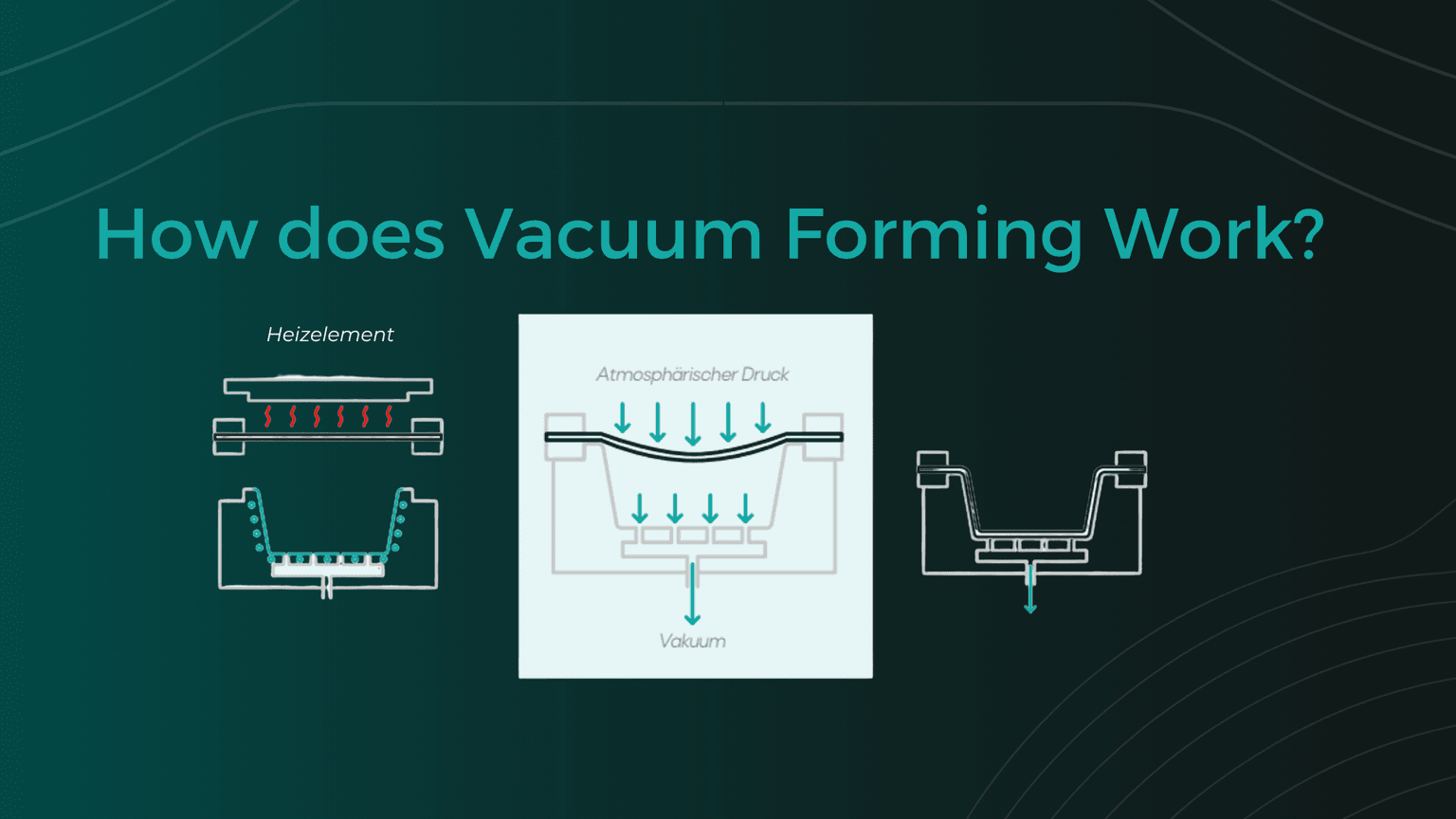
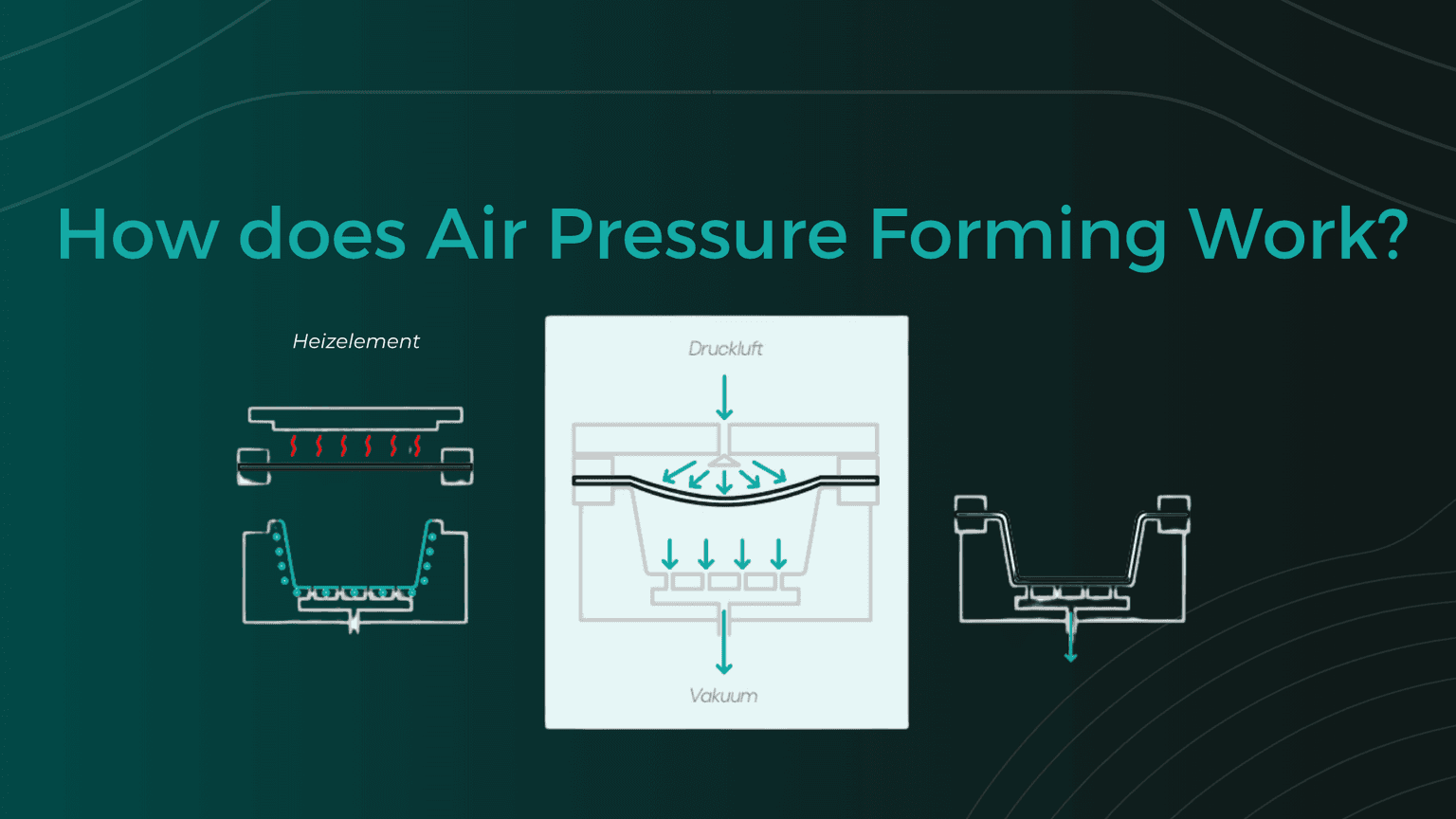
Description
Polystyrene (PS) is considered the standard reference plastic in plastic thermoforming and is universally applicable. Many thermoforming projects begin with PS plastic. When polystyrene is mentioned in thermoforming, it always refers to the high-impact modified type, PS-HI (high impact). PS plastic has a medium temperature range of up to 80°C. Its medium hardness and strength make it a cost-effective choice for thermoformed packaging and transport applications with low mechanical requirements.
Processing and Thermoformability
PS plastic is the reference material for plastic thermoforming due to its excellent thermoforming properties. PS plastic films or sheets require short heating and cooling cycles in the thermoforming machine, allowing for high processing speed. Since PS has similar shrinkage properties to PET-G, PET, and ABS plastics, these materials can often be processed using tooling designed for PS plastic. For this reason, PS plastic can be considered a "bottom-up" plastic, from which one can switch to a thermoplastic with enhanced mechanical properties and stability (e.g., ABS plastic) when needed. When post-processing or assembling PS blister packs, the material stands out for its excellent adhesion properties. The procurement price of thermoformable PS is highly dependent on the price of its precursor, styrene. In summer, seasonal price peaks may occur due to its use in the construction industry.
Material Options
 Antistatic
Antistatic ESD
ESD Flocked
Flocked Sealability
Sealability Adhesive
Adhesive Printable
Printable Regenerate
RegenerateFacts
Price
Colors
Features
- High rigidity
- High hardness
- Chemical resistance
- Component assembly: Excellent adhesion properties
- Available features: Flocked, metallized, electrically conductive
- Can be substituted with PET(-G) or ABS using the same tooling
- Low minimum order quantities
Weaknesses
- Poor mechanical properties
- Low stability
- Brittle and prone to breaking under stress
- Highly volatile pricing at times
Common Industries and Applications:
Electronics
- Refrigerator covers
- Meter cabinet side panels
- Housings for electronic components
- PCB trays
- ESD trays
- Battery trays
- Housing parts and circuit boards
- Splash protection for batteries
- Automation trays with adhesion grippers
- Frames for PCB encapsulation
- Packaging inlays for electronic devices
Medical Technology
- Medical hardware: stationary eye wash stations with clear lids
- Drawer inserts
- Trays for medical parts
- Inserts for dental components
- Containers for micro-surgical instruments
- Sanitary trays
- Pharmaceutical shipping container lids

Consumer Goods
- Decorative furniture covers
- Flower and plant inserts
- Game inserts
- Suitcase inserts for tool sets
- Packaging inserts
- Cosmetic trays and packaging
- Blister packs for small parts

Mechanical Engineering
- Protective covers for control panels
- Maintenance boxes
- Automation trays
- Transport trays
- Trays for metal housings
- Tool case inserts

Food
- Display inserts

Industrial Solutions
- Standard transport trays
- Floor inserts for small load carriers (KLTs)
- Automated assembly line trays
- Packaging for stainless steel components
- Drop trays
- Cover hoods

Automotive
- Bumper covers
- Tanks and lids
- Battery covers
- Dust protection hoods
- Housings for model vehicles
- Windshields
- Motorcycle covers
Facts and Figures:
| Group | Standard Thermoplastics |
| Structure | Amorphous |
| Density | 1.05 |
| Continuous Use Temperature Min. (in °C) | -20 |
| Continuous Use Temperature Max. (in °C) | 60 |
| Thermal Expansion Transverse/Longitudinal to Flow Direction (10^-6 *K) | 80 |
| Melting Temperature (°C) | 100 |
| Max. Temp. Short-Term (°C) | 80 |
| Max. Temp. Long-Term (°C) | 70 |
| Impact Strength (KJ/m^2) | 10 |
| Abrasion Resistance | - |
| Yield Stress (N/mm²) | 26 |
| Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | 32 |
| Tensile Modulus of Elasticity (N/mm²) | 2150 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 3 |
| Flexural Strength (N/mm²) | 103 |
| Ball Indentation Hardness (N/mm²) | 150 |
| Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | 43 |
| Volume Resistivity (Ω · m) | >1E14 |
| Surface Resistivity (Ω) | >1E14 |
| Tracking Resistance CTI | 425 |
Additional Plastics in the formary Portfolio
Häufige Fragen zu PS Kunststoff
PS plastic (polystyrene) is a standard plastic that can be used universally in thermoforming. Due to its good processability and low price, it is often used for packaging, trays, covers and technical housings, especially in the electronics, medical technology and consumer goods industries.