Thermoforming Plastic Sheets
Forming from the plastic sheet up to 4000 x 3000mm forming area | up to 15mm initial thickness | Fast prototypes | Surface finishes


What does thermoforming of plastic sheets mean?
Thermoforming with plastic sheets is used in the manufacture of large, voluminous parts.
Thermoforming plastic sheets produces large, voluminous plastic components. From a material thickness of approx. 3 mm, rolls are no longer used; instead, sheets are used. These can be up to 15 mm thick and 4,000 x 3,000 mm in size.
Deep-drawn sheets are particularly suitable for covers, housings, and large-volume workpiece carriers that need to be lightweight, stable, and precise.
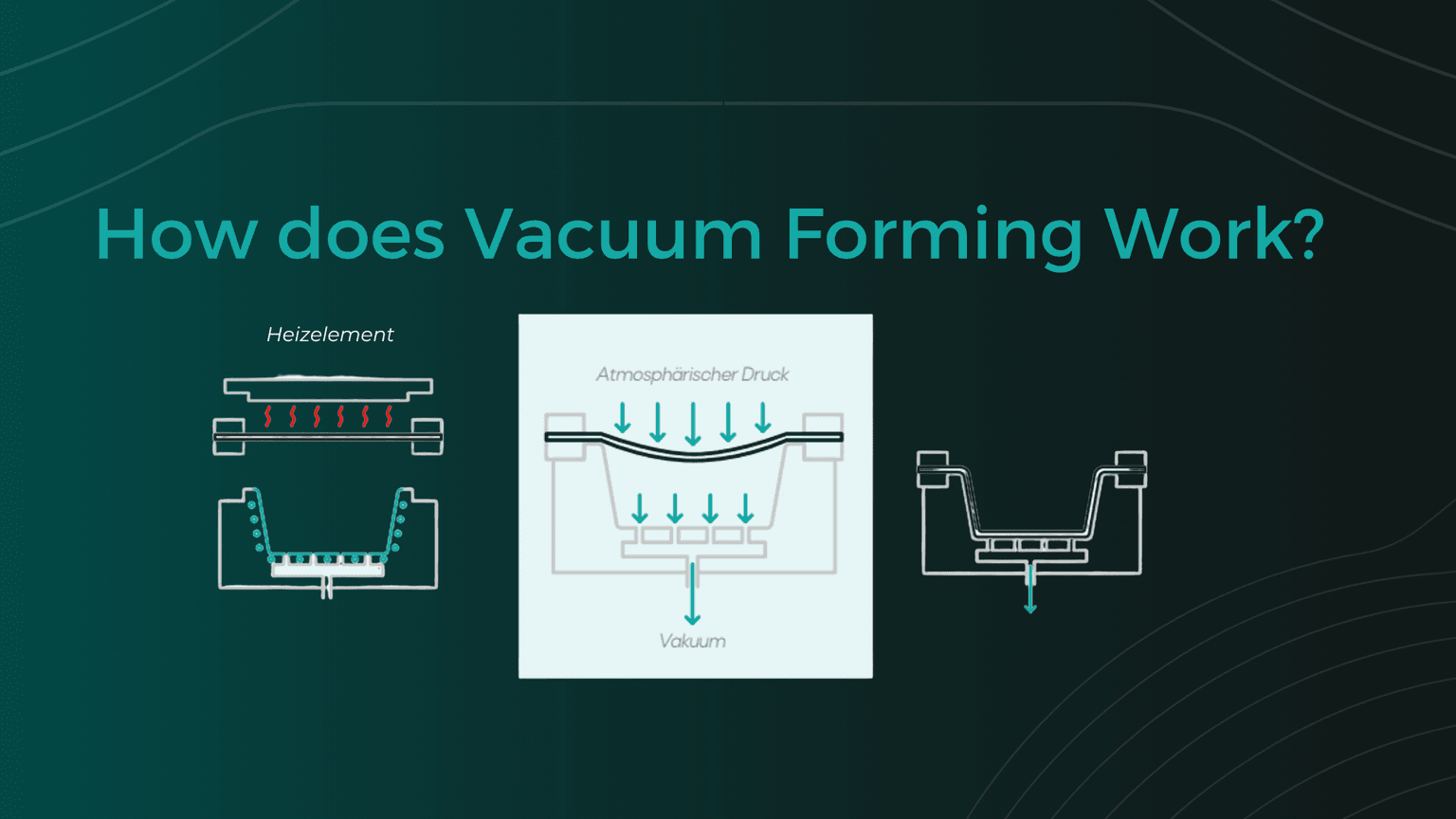
How the forming process works
Plastic sheet is clamped in a frame
Sheet is heated
Material is pre-stretched with compressed air
Tool forms the thermoformed part
Frame opens, thermoformed part is removed
Key facts on forming from plastic sheets
4 x 3 m
50 to > 10.000
1.200mm
15mm
From 4 weeks
When is thermoforming plastic sheets worthwhile?
| Procedure | Advantages | Typical applications | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoforming sheets | Large parts up to 4000 × 3000 mm, wall thicknesses up to 15 mm, low tooling costs | Machine covers, caravan parts, medical technology housings | Longer cycle times, not for million-unit series production |
| Thermoforming films | Very fast cycle times, economical for thin wall thicknesses, fully automatic | Blister packs, trays, packaging | More suitable for small to medium-sized parts |
Advantages of forming from plastic sheets
Cost savings
Lower project costs compared to metal parts, fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP), or small to medium injection molding series.
Suitable for small batches
Depending on the application, forming from plastic sheets is cost-effective from just a few hundred units up to several thousand.
Material variety
Sheet-forming machines process materials directly with texture and color—no post-processing needed.
Unlimited post-processing options
Surface finishing options include grinding, polishing, painting, printing, and electroplating.
Lightweight components
Thermoforming on plastic sheets enables the production of large, thin-walled, and lightweight parts.
Precision cutting
Fast and precise contours, openings, slots, and recesses are achievable with 5-axis CNC milling machines.
Product applications for plastic sheet forming
Transport
- Automotive,
- Electronics,
- Medical Technology,
- Industrial Solutions,
- Consumer Goods
Automation
- Automotive,
- Electronics,
- Industrial Solutions,
- Mechanical Engineering
Boxes
- Medical Technology,
- Mechanical Engineering,
- Consumer Goods
Inlays
- Industrial Solutions,
- Electronics,
- Consumer Goods,
- Cosmetics,
- Medical Technology
Covers
- Automotive,
- Industrial Solutions,
- Medical Technology,
- Consumer Goods,
- Electronics,
- Mechanical Engineering
Examples from plastic sheet production
Available thermoplastics for plastic sheet Forming
The formary network offers plastic sheets in various materials to meet the needs of different industries and applications.
Tooling setup for plastic sheet forming machines
The base plate is the first component of the so-called substructure. In sheet-forming machines, the base plate is an integral part of the forming machine and does not need to be separately manufactured when ordering a forming tool.
More information on forming from plastic sheets
Key factors in your cost calculation for forming from plastic sheets
Cycle time
Setup times
Machine fit
Digital control
Preheating
Cooling
Energy Consumption
Data Storage
Undercuts
Quality and tolerances in plastic sheet forming
| Part areas | Relevant points and tolerances |
|---|---|
| Dimensional measurements | Tolerances according to DIN ISO 2768-c or -m |
| Material thickness | - Semi-finished material: Manufacturers typically allow a tolerance range of up to +/-10% in material thickness. - This must be checked before production to proactively adjust for thickness variations within a tighter tolerance range. - These fluctuations must be considered within the tolerance window. |
| Trim edge | - Milling: Milled edges are deburred. The precision and cleanliness of the milling cut depend on the chosen milling head size and milling speed. - Knife-cut punching: In knife-cut punching, attention must be paid to whiskers (fine filaments) along the trim contour. - Shear-cut punching: In shear-cut punching, burr formation at the trim edge must be considered. |
Frequently asked questions about thermoforming sheets
Thermoformed sheets are thicker materials (3 mm and above) and large-volume parts such as covers and containers. Rolls/films are intended for thin-walled, small plastic trays and blister packs.