Thermoplastics in the formary Portfolio
Each thermoplastic has unique properties that make it particularly suitable for specific applications. Choosing the right material is crucial to the success of your thermoforming project.
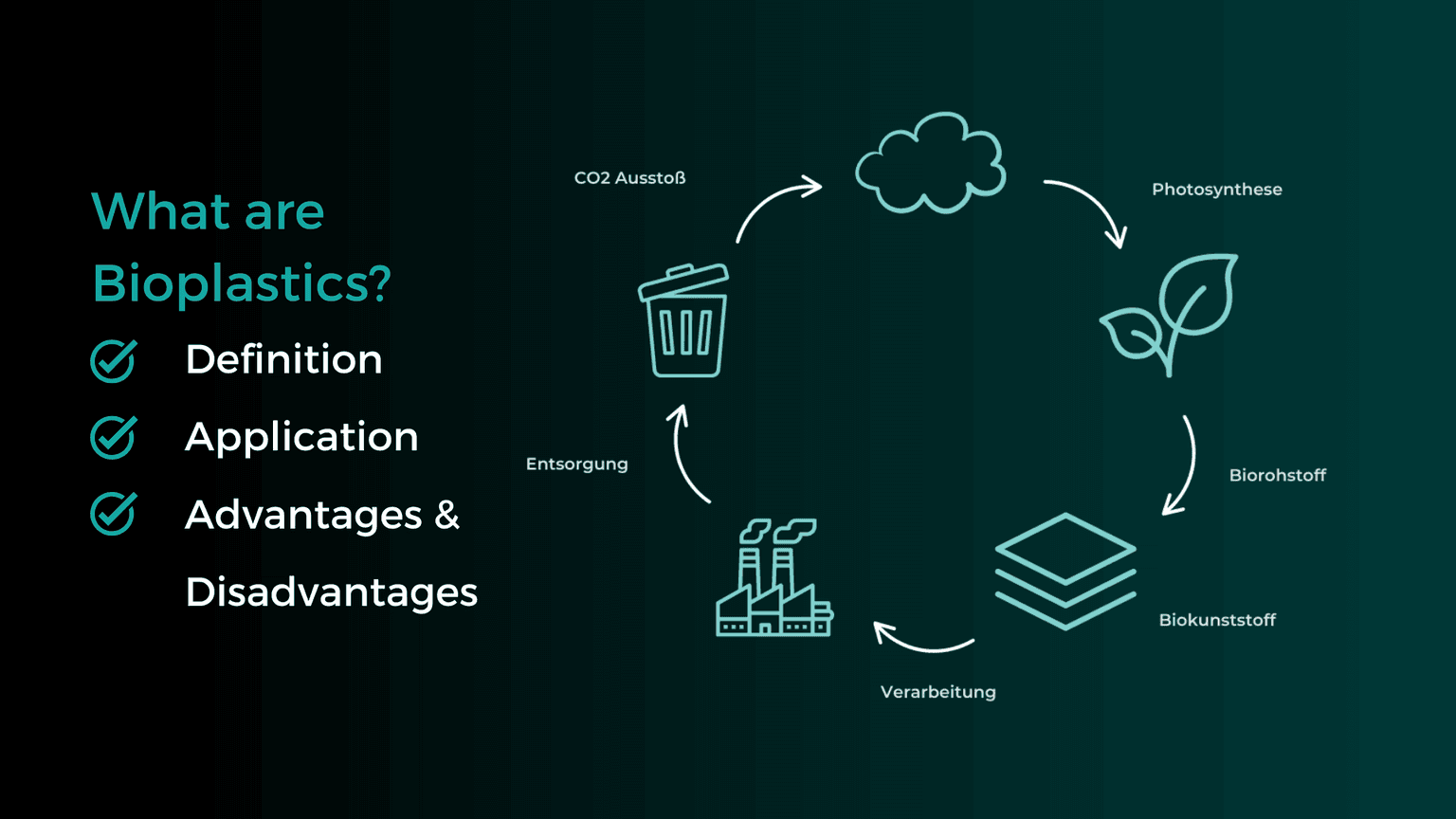
What are Thermoplastics?
Thermoplastics, also known as plastomers, are plastics that become formable when heated and solidify again when cooled. This formability makes thermoplastic materials ideal for the thermoforming process, as they can be heated and shaped multiple times without permanently altering their material structure.
Thermoplastic Properties
Thermoplastic materials combine versatile physical and chemical properties, making them attractive for a wide range of industries.
Design freedom
Thermoplastics can be heated and formed into almost any shape. This makes them ideal for manufacturing customized plastic trays, covers, inserts, or housings.
Mechanical durability
Depending on the material, thermoplastics can be flexible, impact-resistant, or highly rigid. They withstand impacts and retain their shape even under continuous load.
Chemical resistance
Many thermoplastics are resistant to acids, oils, and cleaning agents. They absorb very little moisture and therefore remain dimensionally stable even in humid environments.
Electrical insulation
Thermoplastics are often good electrical insulators, which is why they are frequently used in electronic components.
Lightweight
Compared to materials such as metal, thermoplastics are significantly lighter and therefore do not add substantial weight to a product.
Recyclability
Due to their thermal formability, thermoplastics can be recycled and reused as recyclate.
Which Plastics are Thermoplastics?
Thermoplastics include: ABS, ASA, HDPE, PC, PET-A, PET-G, PMMA, PP, PS, and PVC. You can find more information about their properties in the overview:
Amorphous & Semi-Crystalline Thermoplastics: the Difference
Thermoplastics are divided into two structural groups: amorphous and semi-crystalline.
Amorphous thermoplastics:
- Soft and formable already at lower temperatures
- Easy to process due to rapid formability during thermoforming
- Low shrinkage and good flow behavior
- Examples: ABS, PS, PMMA, PC
Semi-crystalline thermoplastics:
- Remain solid for a longer time
- Then melt relatively quickly at higher temperatures
- Therefore have a short processing window for thermoforming
- Higher shrinkage, requiring more demanding mold cooling
- Examples: PP, HDPE, PET-A, PET-G, PVC
Factors Influencing the Thermoformability of Plastics
The processability of a plastic depends largely on the following factors:
Temperature window
The size of the temperature range in which the material can be uniformly formed affects process stability.
Shrinkage
After cooling, the material contracts to varying degrees. This volume change must be taken into account during tool design.
Sagging & softening
Materials that sag significantly when heated require adapted mold cooling or pre-stretching.
Stretching behavior
The more evenly the plastic stretches, the more uniform the wall thickness will be.
Which Plastics are Particularly Suitable for Thermoforming?
In thermoforming, almost all common thermoplastic plastics can be used.
The key requirement is that the material is available in extruded sheet or film form, as thermoforming always processes pre-produced semi-finished materials.
Polystyrene (PS) is especially well suited for thermoforming and is considered the reference plastic in this process. PS offers a wide temperature window, is easy to form, and delivers uniform wall thicknesses. Polypropylene (PP) is more challenging due to its high shrinkage of around 2% and its tendency to sag during heating.
More Information about Thermoplastics
Material guide – Compact thermoforming knowledge
Webinar
In this webinar, you will receive an introduction to the thermoforming process and gain insights into the plastics value chain and the current market situation for thermoplastics.
Material guide for thermoformed plastic parts (1/2)
White paper
The material guide for thermoformed plastic parts provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of thermoplastics and their specific properties.
How Do I Find the Right Thermoplastic?
Not sure which plastic is right for your application? No problem – at formary, we have built up years of know-how and expertise that you can rely on. Here’s how it works:
Configure your product
The configurator asks for all relevant information needed to select the most suitable thermoplastic for your product.
Involve thermoforming experts
Simply choose “Get a recommendation” in the material selection step and let formary handle the decision.
Receive a quote for the optimal thermoplastic
Based on your specifications, we determine the optimal thermoplastic material for your product.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Thermoformable thermoplastics
A thermoplastic is a plastic that can be shaped when heated and solidifies again when cooled. This process is reversible, meaning thermoplastics can be heated and reshaped multiple times. As a result, thermoplastic materials are ideally suited for the thermoforming process.