Printing on Plastic Parts – The Difference Between Pad Printing and Screen Printing
Printing on thermoformed plastic parts enables detailed lettering, designs, and branding elements. Pad and screen printing are the most commonly used methods, depending on the application. This article explores these techniques in more detail.

Sarah Guaglianone
13. Januar 2026
Contents
Why Print on Plastic Parts?
Printing on plastic parts is considered an “off-mold decoration” process, which is applied after the forming process. Especially for products such as covers, trays, and housings manufactured through plastic deep drawing, printing is an optimal surface refinement solution for customizing the appearance of deep-drawn parts.
The print on plastic parts must not only be aesthetically appealing but also highly durable and scratch-resistant. After all, the print—whether a logo, scales, or control elements—significantly contributes to the overall appearance of the product. Choosing the right printing process is therefore crucial.
Which Plastics Can Be Printed?
You can print on:
- ABS plastic
- PC plastic
- PE plastic
- PP plastic
- and more.
Printing on plastic parts is possible with many thermoplastics. However, it is important to note that not all plastics are equally suitable for printing.
Some plastics have a naturally low surface tension, making it difficult for inks to adhere. In such cases, special pre-treatments such as cleaning, degreasing, or using adhesion promoters are recommended to improve ink adhesion.
Printing Plastic Parts with Screen Printing or Pad Printing – A Comparison
Two of the most common methods for printing on plastic parts are screen printing and pad printing. Both processes have specific properties and are suitable for different applications. Which one is better for your project? Find out below:
Screen Printing on Plastic – Ideal for Printing on Flat Surfaces
What is screen printing?
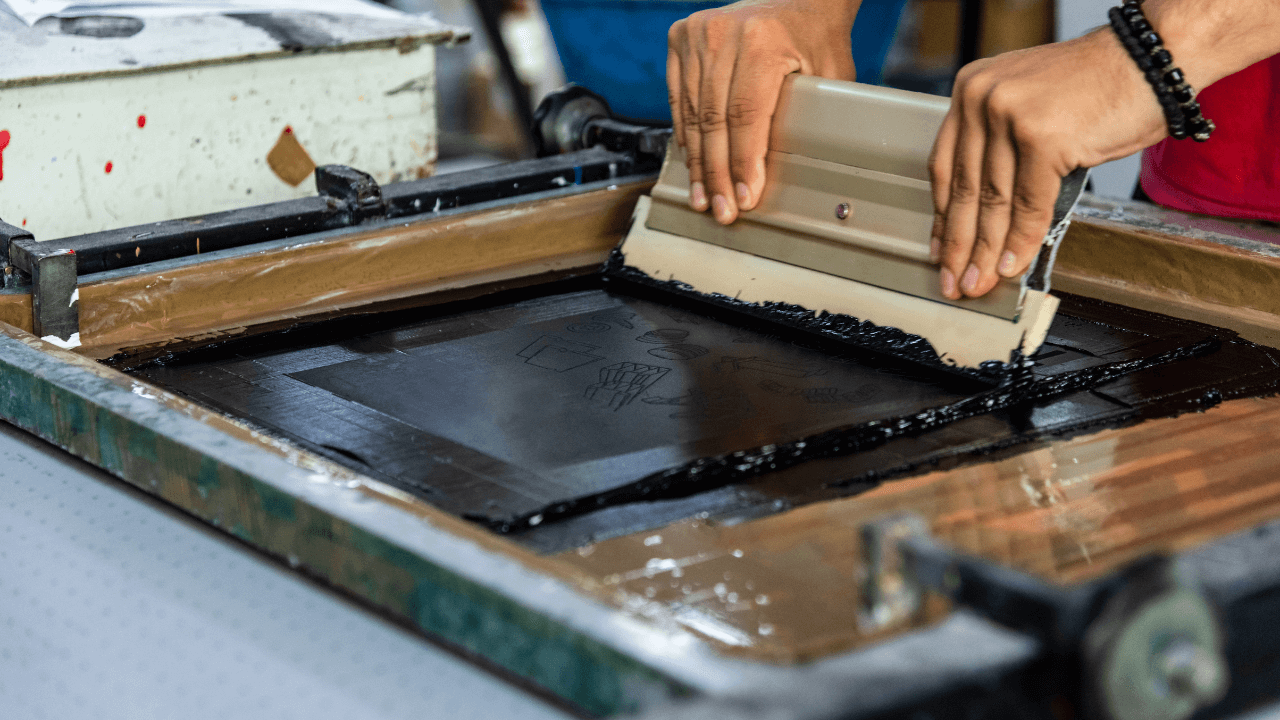
Screen printing is a stencil-based process that allows precise transfer of designs onto various surfaces. It is also called stencil printing because certain areas of the screen are covered with a stencil, allowing ink to pass through only the open sections.

Screen printing on plastic is particularly effective on flat surfaces and is often used on larger areas such as covers and housings, as the somewhat coarse textile structure limits the ability to reproduce very fine or small screen-printed motifs with precision.
How Does Screen Printing Work?
- Screen Preparation: A fine-mesh screen (usually made of polyester or polyamide) is stretched onto a frame. A light-sensitive coating is applied to this screen.
- Creating the Stencil: The desired print design is transferred onto the screen through exposure. Non-exposed areas remain ink-permeable, while exposed areas block ink.
- Printing Process: The screen is placed on the plastic part. A squeegee (a rubber blade) spreads ink over the screen, pressing it through the open areas onto the material.
- Drying: The printed part is dried to fix the ink, either through air drying or in specialized drying units.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Screen Printing
| Screen Printing Advantages | Screen Printing Disadvantages |
| High color intensity: Vibrant colors on dark materials. | Complex preparation: Time-consuming and costly. |
| Durability: Resistant to abrasion and weather conditions. | Limited detail accuracy: Fine details can be difficult to reproduce. |
| Special colors & effects: Metallic, fluorescent inks possible. | Time-consuming multi-color printing: Each color requires a separate pass. |
| High reproducibility: Ideal for large print runs. | Limited flexibility: Expensive design changes. |
Pad Printing on Plastic – Ideal for Uneven and Complex Surfaces
What is pad printing?
Pad printing is a versatile and highly flexible printing process, especially suitable for uneven and complex surfaces. It is an indirect printing method where an elastic silicone pad transfers the ink onto the material.

How Does Pad Printing Work?
- Ink Transfer: Ink is applied to an engraved printing plate (cliché).
- Ink Pickup: A silicone pad picks up the ink from the engraving.
- Printing Process: The pad presses the ink onto the plastic part.
- Adaptation to Shape: The flexible pad conforms to curved, concave, or convex surfaces.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Pad Printing
| Pad Printing Advantages | Pad Printing Disadvantages |
| Flexible for complex shapes: Suitable for curved and irregular objects. | Limited print size: More suitable for smaller areas. |
| Fine lines and detailed motifs: Precise reproduction of small and intricate designs. | Thinner ink layer: Less intense color compared to screen printing. |
| High durability: Resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and external influences. | / |
| Efficiency: Multi-color prints possible in one step. | / |
| Quick drying: Inks dry quickly at room temperature. | / |
Pad Printing vs. Screen Printing – Applications at a Glance
The main difference between pad printing and screen printing lies in their applications and the type of surfaces they can print on.
When to Use Pad Printing?
Pad printing is more versatile when printing on irregular and complex shapes. Specific applications include:
- Automotive Plastic Deep-Drawn Parts: Buttons, switches, and control knobs inside vehicles, such as climate control dials or radio buttons. These parts often have curved or uneven surfaces, which pad printing can accurately print on.
- Medical Plastic Deep-Drawn Parts: Used for medical device housings, such as covers for inhalers and dialysis machines.
- Electronic Plastic Deep-Drawn Parts: Enables fine details such as characters and symbols on irregular surfaces. Applications include ESD workpiece carriers and ESD transport packaging.
When to Use Screen Printing?
Screen printing is better suited for flat and large surfaces requiring high color density. Examples include:
- Plastic housings for electronics: Large casings for household appliances, computers, and entertainment electronics.
- Large-format covers: Such as caravan covers and tractor panels.
The choice between pad printing and screen printing depends on the shape of the thermoformed part, the desired print quality, and the area of application.
Printing Plastic Parts with Screen Printing or Pad Printing – A Conclusion
So, which is better – pad printing or screen printing? Pad printing is best for printing on uneven and complex surfaces, allowing for highly detailed prints but with smaller print sizes and lower color intensity.
Screen printing is ideal for large and flat surfaces, offering intense colors, but requires more preparation and is less suitable for fine details.
Not sure which printing method is right for your project?
Contact us – we’ll be happy to assist you!